Chapter 5 Demand
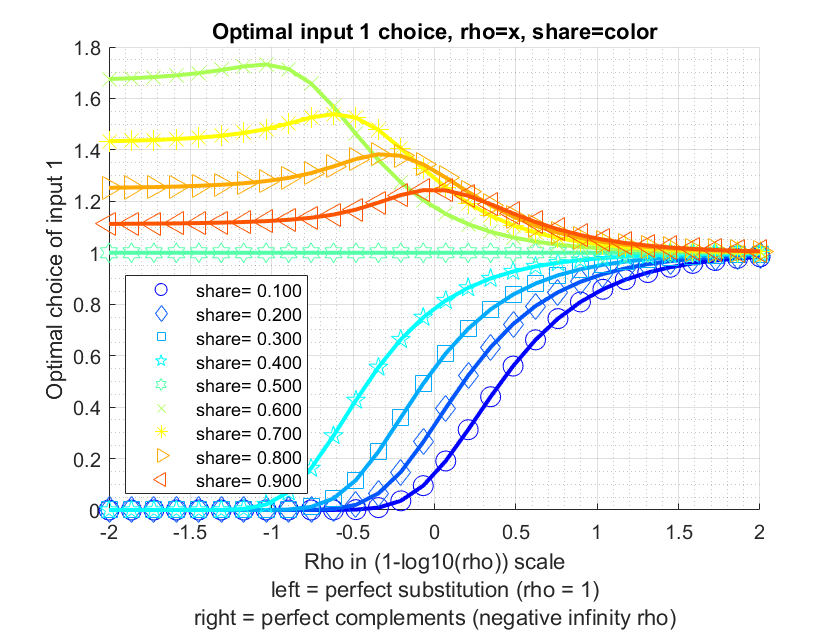
5.1 Solve Nested CES Optimal Demand (CRS)
Testing the bfw_crs_nested_ces function from the PrjLabEquiBFW Package. This function solves optimal choices given CES production function under cost minimization. Works with Constant Elasticity of Substitution problems with constant returns, up to four nest layers, and two inputs in each sub-nest. Takes as inputs share and elasticity parameters across layers of sub-nests, as well as input unit costs at the bottom-most layer. Works with Constant Elasticity of Substitution problems with constant returns, up to four nest layers, and two inputs in each sub-nest. Allows for uneven branches, so that some branches go up to four layers, but others have less layers, works with BFW (2022) nested labor input problem.
5.1.1 Key Inputs and Outputs for bfw_mp_func_demand
Here are the key inputs for the CES demand solver function:
FL_YZ float output divided by productivity, aggregate single term
CL_MN_PRHO cell array of rho (elasticity) parameter between negative infinity and 1. For example, suppose there are four nest layers, and there are two branches at each layer, then we have 1, 2, 4, and 8 \(\rho\) parameter values at the 1st, 2nd, 3rd, and 4th nest layers: size(CL_MN_PRHO{1})= \(\left\lbrack 1,1\right\rbrack\), size(CL_MN_PRHO{2}) = \(\left\lbrack 1,2\right\rbrack\), size(CL_MN_PRHO{3}) = \(\left\lbrack 2,2\right\rbrack\), size(CL_MN_PRHO{4}) = \(\left\lbrack 2,2,2\right\rbrack\). Note that if the model has 4 nest layers, not all cells need to be specified, some branches could be deeper than others.
CL_MN_PSHARE cell array of share (between 0 and 1) for the first input of the two inputs for each nest. The structure for this is similar to CL_MN_PRHO.
CL_MN_PRICE cell array of wages for both wages for the first and second nest, the last index in each element of the cell array indicates first (1) or second (2) wage. For example, suppose we have four layers, with 2 branches at each layer, as in the example for CL_MN_PRHO, then we have 2, 4, 8, and 16 wage values at the 1st, 2nd, 3rd, and 4th nest layers: size(CL_MN_PRICE{1}) = \(\left\lbrack 1,2\right\rbrack\), size(CL_MN_PRICE{2}) = \(\left\lbrack 2,2\right\rbrack\), size(CL_MN_PRICE{3}) = \(\left\lbrack 2,2,2\right\rbrack\), size(CL_MN_PRICE{4}) = \(\left\lbrack 2,2,2,2\right\rbrack\) . Note that only the last layer of wage needs to be specified, in this case, the 16 wages at the 4th layer. Given optimal solutions, we solve for the 2, 4, and 8 aggregate wages at the higher nest layers. If some branches are deeper than other branches, then can specific NA for non-reached layers along some branches.
BL_BFW_MODEL boolean true by default if true then will output outcomes specific to the BFW 2022 problem.
Here are the key outputs for the CES demand solver function:
CL_MN_YZ_CHOICES has the same dimension as CL_MN_PRICE, suppose there are four layers, the CL_MN_PRICE{4} results at the lowest layer includes quantity choices that might be observed in the data. CL_MN_PRICE cell values at non-bottom layers include aggregate quantity outcomes.
CL_MN_PRICE includes at the lowest layer observed wages, however, also includes higher layer aggregate solved waves. CL_MN_PRHO and CL_MN_PSHARE are identical to inputs.
5.1.2 Single Nest Layer Two Inputs CES Problem (Demand)
In this first example, we solve a constant returns to scale problem with a single nest, meaning just two inputs and a single output.
clc;
close all;
clear all;
% Output requirement
fl_yz = 1;
% rho = 0.5, 1/(1-0.5)=2, elasticity of substitution of 2
cl_mn_prho = {[0.1]};
% equal share, similar "productivity"
cl_mn_pshare = {[0.5]};
% wages for the two inputs, identical wage
cl_mn_price = {[1.5, 0.75]};
% print option
bl_verbose = true;
mp_func = bfw_mp_func_demand();
bl_bfw_model = false;
[cl_mn_yz_choices, cl_mn_price] = ...
bfw_crs_nested_ces(fl_yz, cl_mn_prho, cl_mn_pshare, cl_mn_price, ...
mp_func, bl_verbose, bl_bfw_model);
----------------------------------------
xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
CONTAINER NAME: mp_container_map ND Array (Matrix etc)
xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
i idx ndim numel rowN colN sum mean std coefvari min max
_ ___ ____ _____ ____ ____ ______ ______ _______ ________ _______ ______
price_c1 1 2 2 2 1 2 2.25 1.125 0.53033 0.4714 0.75 1.5
yz_c1 2 4 2 2 1 2 2.1343 1.0671 0.55403 0.51918 0.67537 1.4589
xxx TABLE:price_c1 xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
c1 c2
___ ____
r1 1.5 0.75
xxx TABLE:yz_c1 xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
c1 c2
_______ ______
r1 0.67537 1.4589
----------------------------------------
xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
CONTAINER NAME: mp_container_map Scalars
xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
i idx value
_ ___ _____
prho_c1 1 1 0.1
pshare_c1 2 3 0.5 5.1.4 Doubly Nest Layer Two Inputs Each Sub-nest CES Problem (Demand)
In this third example, solve for optimal choices for a doubly nested problem. Below, we first solve for the optimal choices, then we do a number of checks, to make sure that the solutions are correct, as expected.
% output requirement
fl_yz = 2.1;
% upper nest 0.1, lower nests 0.35 and -1 separately for rho values
cl_mn_prho = {[0.1], [0.35, -1]};
% unequal shares of share values
cl_mn_pshare = {[0.4], [0.3, 0.88]};
% differential wages
% in lower-left nest, not productive and very expensive, not very elastic
% last index for left or right,
cl_mn_price = {[nan, nan], [10, 1;3, 4]};
% print option
bl_verbose = true;
[cl_mn_yz_choices, cl_mn_price, cl_mn_prho, cl_mn_pshare] = ...
bfw_crs_nested_ces(fl_yz, cl_mn_prho, cl_mn_pshare, cl_mn_price, ...
mp_func, bl_verbose, bl_bfw_model);
----------------------------------------
xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
CONTAINER NAME: mp_container_map ND Array (Matrix etc)
xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
i idx ndim numel rowN colN sum mean std coefvari min max
_ ___ ____ _____ ____ ____ ______ ______ _______ ________ ________ ______
prho_c2 1 2 2 2 1 2 -0.65 -0.325 0.95459 -2.9372 -1 0.35
price_c1 2 3 2 2 1 2 7.7788 3.8894 2.0959 0.53886 2.4074 5.3714
price_c2 3 4 2 4 2 2 18 4.5 3.873 0.86066 1 10
pshare_c2 4 6 2 2 1 2 1.18 0.59 0.41012 0.69512 0.3 0.88
yz_c1 5 7 2 2 1 2 4.4862 2.2431 0.68863 0.307 1.7561 2.73
yz_c2 6 8 2 4 2 2 9.0506 2.2626 2.7086 1.1971 0.047893 6.0934
xxx TABLE:prho_c2 xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
c1 c2
____ __
r1 0.35 -1
xxx TABLE:price_c1 xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
c1 c2
______ ______
r1 2.4074 5.3714
xxx TABLE:price_c2 xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
c1 c2
__ __
r1 10 1
r2 3 4
xxx TABLE:pshare_c2 xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
c1 c2
___ ____
r1 0.3 0.88
xxx TABLE:yz_c1 xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
c1 c2
____ ______
r1 2.73 1.7561
xxx TABLE:yz_c2 xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
c1 c2
________ _______
r1 0.047893 6.0934
r2 2.2044 0.70496
----------------------------------------
xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
CONTAINER NAME: mp_container_map Scalars
xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
i idx value
_ ___ _____
prho_c1 1 1 0.1
pshare_c1 2 5 0.4
% there are four optimal choices, they are
fl_opti_x11 = cl_mn_yz_choices{2}(1,1);
fl_opti_x12 = cl_mn_yz_choices{2}(1,2);
fl_opti_x21 = cl_mn_yz_choices{2}(2,1);
fl_opti_x22 = cl_mn_yz_choices{2}(2,2);
% display
st_print = strjoin(...
["completed double nest test:", ...
['nest 1 input 1, fl_opti_x11=' num2str(fl_opti_x11)], ...
['nest 1 input 2, fl_opti_x12=' num2str(fl_opti_x12)], ...
['nest 2 input 1, fl_opti_x21=' num2str(fl_opti_x21)], ...
['nest 2 input 2, fl_opti_x22=' num2str(fl_opti_x22)], ...
], ";");
st_out = st_print;
ar_ch_out = char(strsplit(st_print,";")');
disp(ar_ch_out);
completed double nest test:
nest 1 input 1, fl_opti_x11=0.047893
nest 1 input 2, fl_opti_x12=6.0934
nest 2 input 1, fl_opti_x21=2.2044
nest 2 input 2, fl_opti_x22=0.70496 5.1.5 Doubly Nest Layer Two Inputs Each Sub-nest CES Problem–Solution Check (Demand)
Checking output equality, if there are problems, would output an error.
% A. Check output Equality
fl_pshare_0 = cl_mn_pshare{1}(1);
fl_pshare_1 = cl_mn_pshare{2}(1);
fl_pshare_2 = cl_mn_pshare{2}(2);
fl_prho_0 = cl_mn_prho{1}(1);
fl_prho_1 = cl_mn_prho{2}(1);
fl_prho_2 = cl_mn_prho{2}(2);
fl_output_1 = ((fl_pshare_1)*fl_opti_x11^(fl_prho_1) + (1-fl_pshare_1)*fl_opti_x12^(fl_prho_1))^(1/fl_prho_1);
fl_output_2 = ((fl_pshare_2)*fl_opti_x21^(fl_prho_2) + (1-fl_pshare_2)*fl_opti_x22^(fl_prho_2))^(1/fl_prho_2);
fl_output_0 = ((fl_pshare_0)*fl_output_1^(fl_prho_0) + (1-fl_pshare_0)*fl_output_2^(fl_prho_0))^(1/fl_prho_0);
if (~if_is_close(fl_output_0, fl_yz))
error('There is an error, output is not equal to required expenditure minimizing output')
endChecking FOC within-nest optimality, if there are problems, would output an error.
% B. Check FOC Optimality inner nest
fl_wage_x11 = cl_mn_price{2}(1,1);
fl_wage_x12 = cl_mn_price{2}(1,2);
fl_wage_x21 = cl_mn_price{2}(2,1);
fl_wage_x22 = cl_mn_price{2}(2,2);
% B1. Checking via Method 1
fl_rela_opti_foc_1 = (((fl_pshare_1/(1-fl_pshare_1)))*(fl_wage_x12/fl_wage_x11))^(1/(1-fl_prho_1));
fl_rela_opti_foc_2 = (((fl_pshare_2/(1-fl_pshare_2)))*(fl_wage_x22/fl_wage_x21))^(1/(1-fl_prho_2));
if (~if_is_close(fl_rela_opti_foc_1, fl_opti_x11/fl_opti_x12))
error('B1. There is an error, optimal relative not equal to expected foc ratio, nest 1')
end
if (~if_is_close(fl_rela_opti_foc_2, fl_opti_x21/fl_opti_x22))
error('B1. There is an error, optimal relative not equal to expected foc ratio, nest 2')
end
% B2. Equation left to right, right to left, checking via method 2
% Check FOC Optimality cross nests (actually within) T1
fl_dy_dx11 = fl_pshare_1*(fl_opti_x11^(fl_prho_1-1));
fl_dy_dx12 = (1-fl_pshare_1)*(fl_opti_x12^(fl_prho_1-1));
fl_rwage_x11dx12 = fl_dy_dx11/fl_dy_dx12;
if (~if_is_close(fl_rwage_x11dx12, fl_wage_x11/fl_wage_x12))
error('B2. There is an error, relative price x11 and x12 does not satisfy within optimality across nests')
endGenerate aggregate prices, if there are problems, would output an error.
% C. Aggregate prices and optimality within higher tier
% Is optimality satisfied given aggregate prices?
fl_rela_wage_share_11 = ...
((fl_wage_x11/fl_wage_x12)*((1-fl_pshare_1)/(fl_pshare_1)))^(fl_prho_1/(1-fl_prho_1));
fl_rela_wage_share_12 = ...
((fl_wage_x12/fl_wage_x11)*((fl_pshare_1)/(1-fl_pshare_1)))^(fl_prho_1/(1-fl_prho_1));
fl_agg_prc_1 = ...
fl_wage_x11*(fl_pshare_1 + (1-fl_pshare_1)*(fl_rela_wage_share_11))^(-1/fl_prho_1) + ...
fl_wage_x12*(fl_pshare_1*(fl_rela_wage_share_12) + (1-fl_pshare_1))^(-1/fl_prho_1);
fl_rela_wage_share_21 = ...
((fl_wage_x21/fl_wage_x22)*((1-fl_pshare_2)/(fl_pshare_2)))^(fl_prho_2/(1-fl_prho_2));
fl_rela_wage_share_22 = ...
((fl_wage_x22/fl_wage_x21)*((fl_pshare_2)/(1-fl_pshare_2)))^(fl_prho_2/(1-fl_prho_2));
fl_agg_prc_2 = ...
fl_wage_x21*(fl_pshare_2 + (1-fl_pshare_2)*(fl_rela_wage_share_21))^(-1/fl_prho_2) + ...
fl_wage_x22*(fl_pshare_2*(fl_rela_wage_share_22) + (1-fl_pshare_2))^(-1/fl_prho_2);
% What is returned by the omega function that is suppose to have aggregate prices?
mp_func = bfw_mp_func_demand();
params_group = values(mp_func, {'fc_OMEGA', 'fc_d1', 'fc_d2'});
[fc_OMEGA, fc_d1, fc_d2] = params_group{:};
% Aggregate price
fl_aggregate_price_1 = fc_OMEGA(...
fl_wage_x11, fl_wage_x12, ...
fl_prho_1, ...
fl_pshare_1, 1 - fl_pshare_1);
fl_aggregate_price_2 = fc_OMEGA(...
fl_wage_x21, fl_wage_x22, ...
fl_prho_2, ...
fl_pshare_2, 1 - fl_pshare_2); Check relative price within nest and across nests, if there are problems, would output an error.
% D. Check FOC Optimality cross nests
% D1a. Two within-nest relative wages and four cross-nest relative wages
% within
fl_rwage_x11dx12 = fl_wage_x11/fl_wage_x12;
fl_rwage_x21dx22 = fl_wage_x21/fl_wage_x22;
% across
fl_rwage_x11dx21 = fl_wage_x11/fl_wage_x21;
fl_rwage_x11dx22 = fl_wage_x11/fl_wage_x22;
fl_rwage_x12dx21 = fl_wage_x12/fl_wage_x21;
fl_rwage_x12dx22 = fl_wage_x12/fl_wage_x22;
% D1b. Generate relative wages within nest and across nests own equations
fl_dy_dx1_shared = (fl_pshare_0*(fl_output_1)^(fl_prho_0-1))*((fl_output_1)^(1-fl_prho_1));
fl_dy_dx11 = fl_dy_dx1_shared*(fl_pshare_1*fl_opti_x11^(fl_prho_1-1));
fl_dy_dx12 = fl_dy_dx1_shared*((1-fl_pshare_1)*fl_opti_x12^(fl_prho_1-1));
fl_dy_dx2_shared = ((1-fl_pshare_0)*(fl_output_2)^(fl_prho_0-1))*((fl_output_2)^(1-fl_prho_2));
fl_dy_dx21 = fl_dy_dx2_shared*(fl_pshare_2*fl_opti_x21^(fl_prho_2-1));
fl_dy_dx22 = fl_dy_dx2_shared*((1-fl_pshare_2)*fl_opti_x22^(fl_prho_2-1));
% within
fl_rwage_x11dx12_foc = fl_dy_dx11/fl_dy_dx12;
fl_rwage_x21dx22_foc = fl_dy_dx21/fl_dy_dx22;
% across
fl_rwage_x11dx21_foc = fl_dy_dx11/fl_dy_dx21;
fl_rwage_x11dx22_foc = fl_dy_dx11/fl_dy_dx22;
fl_rwage_x12dx21_foc = fl_dy_dx12/fl_dy_dx21;
fl_rwage_x12dx22_foc = fl_dy_dx12/fl_dy_dx22;
if (~if_is_close(fl_rwage_x11dx21_foc, fl_wage_x11/fl_wage_x21))
error('There is an error, relative price x11 and x21 does not satisfy cross optimality across nests')
end
if (~if_is_close(fl_rwage_x12dx22_foc, fl_wage_x12/fl_wage_x22))
error('There is an error, relative price x12 and x22 does not satisfy cross optimality across nests')
end
% D2. Check FOC Optimality cross nests, simplified equation
fl_rela_wage_x11_x21 = log((fl_pshare_0/(1-fl_pshare_0))* ...
((fl_pshare_1*fl_opti_x11^(fl_prho_1-1)*fl_output_2^(fl_prho_2))/(fl_pshare_2*fl_opti_x21^(fl_prho_2-1)*fl_output_1^(fl_prho_1)))) + ...
fl_prho_0*log(fl_output_1/fl_output_2);
if (~if_is_close(fl_rela_wage_x11_x21, log(fl_wage_x11/fl_wage_x21)))
error('There is an error, relative price x11 and x21 does not satisfy cross optimality across nests')
end5.1.6 BFW (2022) Nested Three Branch (Four Layer) Problem (Demand)
The model BFW 2022 has three branches and four layers. one of the branches go down only three layers, the other two branches go down four layers.
First, we prepare the various inputs:
% Controls
bl_verbose = true;
bl_bfw_model = true;
% Given rho and beta, solve for equilibrium quantities
bl_log_wage = false;
mp_func = bfw_mp_func_demand(bl_log_wage);
% Following instructions in: PrjFLFPMexicoBFW\solvedemand\README.md
% Nests/layers
it_nests = 4;
% Input cell of mn matrixes
it_prho_cl = 1;
it_pshare_cl = 2;
it_price_cl = 3;
for it_cl_ctr = [1,2,3]
cl_mn_cur = cell(it_nests,1);
% Fill each cell element with NaN mn array
for it_cl_mn = 1:it_nests
bl_price = (it_cl_ctr == it_price_cl);
if (~bl_price && it_cl_mn == 1)
mn_nan = NaN;
elseif (~bl_price && it_cl_mn == 2) || (bl_price && it_cl_mn == 1)
mn_nan = [NaN, NaN];
elseif (~bl_price && it_cl_mn == 3) || (bl_price && it_cl_mn == 2)
mn_nan = NaN(2,2);
elseif (~bl_price && it_cl_mn == 4) || (bl_price && it_cl_mn == 3)
mn_nan = NaN(2,2,2);
elseif (~bl_price && it_cl_mn == 5) || (bl_price && it_cl_mn == 4)
mn_nan = NaN(2,2,2,2);
elseif (~bl_price && it_cl_mn == 6) || (bl_price && it_cl_mn == 5)
mn_nan = NaN(2,2,2,2,2);
end
cl_mn_cur{it_cl_mn} = mn_nan;
end
% Name cell arrays
if (it_cl_ctr == it_prho_cl)
cl_mn_prho = cl_mn_cur;
elseif (it_cl_ctr == it_pshare_cl)
cl_mn_pshare = cl_mn_cur;
elseif (it_cl_ctr == it_price_cl)
cl_mn_price = cl_mn_cur;
end
end
% Initialize share matrix
rng(123);
for it_cl_mn = 1:it_nests
mn_pshare = cl_mn_pshare{it_cl_mn};
if it_cl_mn == 4
mn_pshare(2,:,:) = rand(2,2);
else
mn_pshare = rand(size(mn_pshare));
end
cl_mn_pshare{it_cl_mn} = mn_pshare;
end
% Initialize rho matrix
rng(456);
for it_cl_mn = 1:it_nests
mn_prho = cl_mn_prho{it_cl_mn};
if it_cl_mn == 4
mn_prho(2,:,:) = rand(2,2);
else
mn_prho = rand(size(mn_prho));
end
% Scalling rho between 0.7500 and -3.0000
% 1 - 2.^(linspace(-2,2,5))
mn_prho = 1 - 2.^(mn_prho*(4) - 2);
cl_mn_prho{it_cl_mn} = mn_prho;
end
% Initialize wage matrix
rng(789);
for it_cl_mn = 1:it_nests
mn_price = cl_mn_price{it_cl_mn};
if it_cl_mn == 3
mn_price(1,:,:) = rand(2,2);
elseif it_cl_mn == 4
mn_price(2,:,:,:) = rand(2,2,2);
end
% Scalling rho between 3 amd 5
mn_price = mn_price*(2) + 3;
cl_mn_price{it_cl_mn} = mn_price;
end
% Initialize yz matrix
rng(101112);
fl_yz = rand();Second, display created inputs:
disp(['fl_yz=' num2str(fl_yz)]);
fl_yz=0.89726
celldisp(cl_mn_prho);
cl_mn_prho{1} =
0.5017
cl_mn_prho{2} =
0.6071 -1.1955
cl_mn_prho{3} =
-1.3523 -0.3346
-0.4167 -1.9136
cl_mn_prho{4} =
(:,:,1) =
NaN NaN
-1.0512 0.5869
(:,:,2) =
NaN NaN
0.6209 0.1633
celldisp(cl_mn_pshare);
cl_mn_pshare{1} =
0.6965
cl_mn_pshare{2} =
0.2861 0.2269
cl_mn_pshare{3} =
0.5513 0.4231
0.7195 0.9808
cl_mn_pshare{4} =
(:,:,1) =
NaN NaN
0.6848 0.4809
(:,:,2) =
NaN NaN
0.3921 0.3432
celldisp(cl_mn_price);
cl_mn_price{1} =
NaN NaN
cl_mn_price{2} =
NaN NaN
NaN NaN
cl_mn_price{3} =
(:,:,1) =
3.6467 3.4605
NaN NaN
(:,:,2) =
4.5876 4.2488
NaN NaN
cl_mn_price{4} =
(:,:,1,1) =
NaN NaN
4.9508 4.5178
(:,:,2,1) =
NaN NaN
3.0212 3.0495
(:,:,1,2) =
NaN NaN
3.2221 4.0763
(:,:,2,2) =
NaN NaN
3.0909 4.1031Third, call function and solve for optimal demand:
% Call function
[cl_mn_yz_choices, cl_mn_price, cl_mn_prho, cl_mn_pshare] = ...
bfw_crs_nested_ces(fl_yz, cl_mn_prho, cl_mn_pshare, cl_mn_price, ...
mp_func, bl_verbose, bl_bfw_model);
----------------------------------------
xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
CONTAINER NAME: mp_container_map ND Array (Matrix etc)
xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
i idx ndim numel rowN colN sum mean std coefvari min max
__ ___ ____ _____ ____ ____ ________ ________ ________ ________ ________ ________
mt_fl_labor_demanded 1 1 2 12 4 3 5.4455 0.45379 0.85359 1.881 0.020122 2.3642
prho_c2 2 3 2 2 1 2 -0.58844 -0.29422 1.2746 -4.3323 -1.1955 0.60709
prho_c3 3 4 2 4 2 2 -4.0173 -1.0043 0.76195 -0.75868 -1.9136 -0.33464
prho_c4 4 5 3 8 2 4 NaN NaN NaN NaN -1.0512 0.62089
price_c1 5 6 2 2 1 2 35.345 17.673 7.0394 0.39832 12.695 22.65
price_c2 6 7 2 4 2 2 40.906 10.226 2.7834 0.27217 7.7015 13.522
price_c3 7 8 3 8 2 4 45.403 5.6754 2.0037 0.35305 3.4605 8.5114
price_c4 8 9 4 16 2 8 NaN NaN NaN NaN 3.0212 4.9508
pshare_c2 9 11 2 2 1 2 0.51299 0.2565 0.041923 0.16344 0.22685 0.28614
pshare_c3 10 12 2 4 2 2 2.6747 0.66866 0.24087 0.36023 0.42311 0.98076
pshare_c4 11 13 3 8 2 4 NaN NaN NaN NaN 0.34318 0.68483
yz_c1 12 14 2 2 1 2 1.6003 0.80016 1.0053 1.2564 0.089284 1.511
yz_c2 13 15 2 4 2 2 2.645 0.66124 1.0849 1.6407 0.057461 2.2864
yz_c3 14 16 3 8 2 4 5.1962 0.64953 1.0063 1.5492 0.03298 2.3642
yz_c4 15 17 4 16 2 8 NaN NaN NaN NaN 0.020122 0.14469
xxx TABLE:mt_fl_labor_demanded xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
c1 c2 c3
________ ________ _______
r1 0.020122 0.024929 2.1857
r2 0.060227 0.037985 2.3642
r3 0.069088 0.093774 0.21107
r4 0.058349 0.14469 0.17539
xxx TABLE:prho_c2 xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
c1 c2
_______ _______
r1 0.60709 -1.1955
xxx TABLE:prho_c3 xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
c1 c2
________ ________
r1 -1.3523 -0.33464
r2 -0.41668 -1.9136
xxx TABLE:prho_c4 xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
c1 c2 c3 c4
_______ _______ _______ _______
r1 NaN NaN NaN NaN
r2 -1.0512 0.58694 0.62089 0.16334
xxx TABLE:price_c1 xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
c1 c2
______ _____
r1 12.695 22.65
xxx TABLE:price_c2 xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
c1 c2
______ ______
r1 8.1518 7.7015
r2 13.522 11.53
xxx TABLE:price_c3 xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
c1 c2 c3 c4
______ ______ ______ ______
r1 3.6467 3.4605 4.5876 4.2488
r2 8.1184 8.5114 5.7986 7.0309
xxx TABLE:price_c4 xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
c1 c2 c3 c4 c5 c6 c7 c8
______ ______ ______ ______ ______ ______ ______ ______
r1 NaN NaN NaN NaN NaN NaN NaN NaN
r2 4.9508 4.5178 3.0212 3.0495 3.2221 4.0763 3.0909 4.1031
xxx TABLE:pshare_c2 xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
c1 c2
_______ _______
r1 0.28614 0.22685
xxx TABLE:pshare_c3 xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
c1 c2
_______ _______
r1 0.55131 0.42311
r2 0.71947 0.98076
xxx TABLE:pshare_c4 xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
c1 c2 c3 c4
_______ _______ _______ _______
r1 NaN NaN NaN NaN
r2 0.68483 0.48093 0.39212 0.34318
xxx TABLE:yz_c1 xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
c1 c2
_____ ________
r1 1.511 0.089284
xxx TABLE:yz_c2 xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
c1 c2
________ ______
r1 0.19312 2.2864
r2 0.057461 0.108
xxx TABLE:yz_c3 xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
c1 c2 c3 c4
_______ _______ ________ _______
r1 0.21107 2.1857 0.17539 2.3642
r2 0.06529 0.11907 0.042587 0.03298
xxx TABLE:yz_c4 xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
c1 c2 c3 c4 c5 c6 c7 c8
________ ________ ________ ________ ________ _______ ________ ________
r1 NaN NaN NaN NaN NaN NaN NaN NaN
r2 0.069088 0.093774 0.020122 0.024929 0.058349 0.14469 0.060227 0.037985
----------------------------------------
xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
CONTAINER NAME: mp_container_map Scalars
xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
i idx value
_ ___ _______
prho_c1 1 2 0.50172
pshare_c1 2 10 0.696475.2 Compute Nested CES MPL Given Demand (CRS)
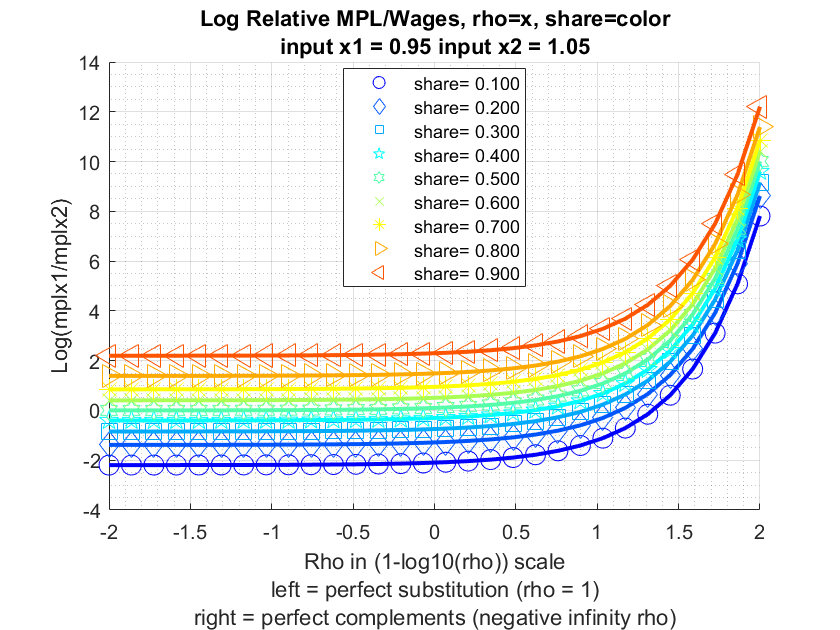
Testing the bfw_crs_nested_ces_mpl function from the PrjLabEquiBFW Package. Given labor quantity demanded, using first-order relative optimality conditions, find the marginal product of labor given CES production function. Results match up with correct relative wages, but not wage levels. Takes as inputs share and elasticity parameters across layers of sub-nests, as well as quantity demanded at each bottom-most CES nest layer. Works with Constant Elasticity of Substitution problems with constant returns, up to four nest layers, and two inputs in each sub-nest. Allows for uneven branches, so that some branches go up to four layers, but others have less layers, works with BFW (2022) nested labor input problem.
5.2.1 Key Inputs and Outputs for bfw_crs_nested_ces_mpl
Here are the key inputs for the CES demand solver function:
CL_MN_PRHO cell array of rho (elasticity) parameter between negative infinity and 1. For example, suppose there are four nest layers, and there are two branches at each layer, then we have 1, 2, 4, and 8 \(\rho\) parameter values at the 1st, 2nd, 3rd, and 4th nest layers: size(CL_MN_PRHO{1})= \(\left\lbrack 1,1\right\rbrack\), size(CL_MN_PRHO{2}) = \(\left\lbrack 1,2\right\rbrack\), size(CL_MN_PRHO{3}) = \(\left\lbrack 2,2\right\rbrack\), size(CL_MN_PRHO{4}) = \(\left\lbrack 2,2,2\right\rbrack\). Note that if the model has 4 nest layers, not all cells need to be specified, some branches could be deeper than others.
CL_MN_PSHARE cell array of share (between 0 and 1) for the first input of the two inputs for each nest. The structure for this is similar to CL_MN_PRHO.
CL_MN_YZ_CHOICES cell array of quantity demanded for the first and second inputs of the bottom-most layer of sub-nests. The last index in each element of the cell array indicates first (1) or second (2) quantities. For example, suppose we have four layers, with 2 branches at each layer, as in the example for CL_MN_PRHO, then we have 2, 4, 8, and 16 quantity values at the 1st, 2nd, 3rd, and 4th nest layers: size(CL_MN_YZ_CHOICES{1})= \(\left\lbrack 1,2\right\rbrack\), size(CL_MN_YZ_CHOICES{2})= \(\left\lbrack 2,2\right\rbrack\), size(CL_MN_YZ_CHOICES{3})= \(\left\lbrack 2,2,2\right\rbrack\), size(CL_MN_YZ_CHOICES{4})= \(\left\lbrack 2,2,2,2\right\rbrack\). Note that only the last layer of quantities needs to be specified, in this case, the 16 quantities at the 4th layer. Given first order conditions, we solve for the 2, 4, and 8 aggregate quantities at the higher nest layers. If some branches are deeper than other branches, then can specific NA for non-reached layers along some branches.
BL_BFW_MODEL boolean true by default if true then will output outcomes specific to the BFW 2022 problem.
Here are the key outputs for the CES demand solver function:
CL_MN_MPL_PRICE has the same dimension as CL_MN_YZ_CHOICES, suppose there are four layers, the CL_MN_MPL_PRICE{4} results at the lowest layer includes wages that might be observed in the data. CL_MN_MPL_PRICE cell values at non-bottom layers include aggregate wages.
CL_MN_YZ_CHOICES includes at the lowest layer observed wages, however, also includes higher layer aggregate solved quantities. CL_MN_PRHO and CL_MN_PSHARE are identical to inputs.
5.2.2 Single Nest Layer Two Inputs CES Problem (MPL)
In this first example, we solve a constant returns to scale problem with a single nest, meaning just two inputs and a single output.
clc;
close all;
clear all;
% rho = 0.5, 1/(1-0.5)=2, elasticity of substitution of 2
cl_mn_prho = {[0.1]};
% equal share, similar "productivity"
cl_mn_pshare = {[0.5]};
% levels of the two inputs, Values picked from demand problem parallel
% example.
cl_mn_yz_choices = {[0.67537, 1.4589]};
% print option
bl_verbose = true;
mp_func = bfw_mp_func_demand();
bl_bfw_model = false;
[cl_mn_yz_choices, cl_mn_mpl_price] = ...
bfw_crs_nested_ces_mpl(cl_mn_prho, cl_mn_pshare, cl_mn_yz_choices, ...
mp_func, bl_verbose, bl_bfw_model);
----------------------------------------
xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
CONTAINER NAME: mp_container_map ND Array (Matrix etc)
xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
i idx ndim numel rowN colN sum mean std coefvari min max
_ ___ ____ _____ ____ ____ ______ _______ _______ ________ _______ _______
mpl_price_c1 1 1 2 2 1 2 1.0678 0.53388 0.25168 0.47141 0.35592 0.71184
yz_c1 2 4 2 2 1 2 2.1343 1.0671 0.55404 0.51918 0.67537 1.4589
xxx TABLE:mpl_price_c1 xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
c1 c2
_______ _______
r1 0.71184 0.35592
xxx TABLE:yz_c1 xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
c1 c2
_______ ______
r1 0.67537 1.4589
----------------------------------------
xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
CONTAINER NAME: mp_container_map Scalars
xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
i idx value
_ ___ _____
prho_c1 1 2 0.1
pshare_c1 2 3 0.5 5.2.4 Doubly Nest Layer Two Inputs Each Sub-nest CES Problem
In this third example, solve for optimal choices for a doubly nested problem. Below, we first solve for the optimal choices, then we do a number of checks, to make sure that the solutions are correct, as expected.
% output requirement
fl_yz = 2.1;
% upper nest 0.1, lower nests 0.35 and -1 separately for rho values
cl_mn_prho = {[0.1], [0.35, -1]};
% unequal shares of share values
cl_mn_pshare = {[0.4], [0.3, 0.88]};
% differential wages
% in lower-left nest, not productive and very expensive, not very elastic
% last index for left or right. Values picked from demand problem parallel
% example.
cl_mn_yz_choices = {[nan, nan], [0.04789, 6.0934; 2.2044, 0.70496]};
% print option
bl_verbose = true;
[cl_mn_yz_choices, cl_mn_mpl_price] = ...
bfw_crs_nested_ces_mpl(cl_mn_prho, cl_mn_pshare, cl_mn_yz_choices, ...
mp_func, bl_verbose, bl_bfw_model);
----------------------------------------
xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
CONTAINER NAME: mp_container_map ND Array (Matrix etc)
xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
i idx ndim numel rowN colN sum mean std coefvari min max
_ ___ ____ _____ ____ ____ ______ _______ _______ ________ _______ _______
mpl_price_c1 1 1 2 2 1 2 1.0206 0.51032 0.27499 0.53886 0.31587 0.70476
mpl_price_c2 2 2 2 4 2 2 2.3618 0.59045 0.5082 0.86069 0.13121 1.3121
prho_c2 3 4 2 2 1 2 -0.65 -0.325 0.95459 -2.9372 -1 0.35
pshare_c2 4 6 2 2 1 2 1.18 0.59 0.41012 0.69512 0.3 0.88
yz_c1 5 7 2 2 1 2 4.4862 2.2431 0.68863 0.307 1.7562 2.73
yz_c2 6 8 2 4 2 2 9.0507 2.2627 2.7086 1.1971 0.04789 6.0934
xxx TABLE:mpl_price_c1 xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
c1 c2
_______ _______
r1 0.31587 0.70476
xxx TABLE:mpl_price_c2 xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
c1 c2
_______ _______
r1 1.3121 0.13121
r2 0.39362 0.52484
xxx TABLE:prho_c2 xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
c1 c2
____ __
r1 0.35 -1
xxx TABLE:pshare_c2 xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
c1 c2
___ ____
r1 0.3 0.88
xxx TABLE:yz_c1 xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
c1 c2
____ ______
r1 2.73 1.7562
xxx TABLE:yz_c2 xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
c1 c2
_______ _______
r1 0.04789 6.0934
r2 2.2044 0.70496
----------------------------------------
xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
CONTAINER NAME: mp_container_map Scalars
xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
i idx value
_ ___ _____
prho_c1 1 3 0.1
pshare_c1 2 5 0.4
% there are four optimal choices, they are
fl_mpl_x11 = cl_mn_mpl_price{2}(1,1);
fl_mpl_x12 = cl_mn_mpl_price{2}(1,2);
fl_mpl_x21 = cl_mn_mpl_price{2}(2,1);
fl_mpl_x22 = cl_mn_mpl_price{2}(2,2);
% display
st_print = strjoin(...
["completed double nest test:", ...
['nest 1 input 1, fl_mpl_x11=' num2str(fl_mpl_x11)], ...
['nest 1 input 2, fl_mpl_x12=' num2str(fl_mpl_x12)], ...
['nest 2 input 1, fl_mpl_x21=' num2str(fl_mpl_x21)], ...
['nest 2 input 2, fl_mpl_x22=' num2str(fl_mpl_x22)], ...
['nest 1 input 1, fl_mpl_x11/fl_mpl_x11=' num2str(fl_mpl_x11/fl_mpl_x11)], ...
['nest 1 input 2, fl_mpl_x12/fl_mpl_x11=' num2str(fl_mpl_x12/fl_mpl_x11)], ...
['nest 2 input 1, fl_mpl_x21/fl_mpl_x11=' num2str(fl_mpl_x21/fl_mpl_x11)], ...
['nest 2 input 2, fl_mpl_x22/fl_mpl_x11=' num2str(fl_mpl_x22/fl_mpl_x11)], ...
], ";");
st_out = st_print;
ar_ch_out = char(strsplit(st_print,";")');
disp(ar_ch_out);
completed double nest test:
nest 1 input 1, fl_mpl_x11=1.3121
nest 1 input 2, fl_mpl_x12=0.13121
nest 2 input 1, fl_mpl_x21=0.39362
nest 2 input 2, fl_mpl_x22=0.52484
nest 1 input 1, fl_mpl_x11/fl_mpl_x11=1
nest 1 input 2, fl_mpl_x12/fl_mpl_x11=0.099995
nest 2 input 1, fl_mpl_x21/fl_mpl_x11=0.29998
nest 2 input 2, fl_mpl_x22/fl_mpl_x11=0.39999 5.2.5 BFW (2022) Nested Three Branch (Four Layer) Problem (MPL)
The model BFW 2022 has three branches and four layers. one of the branches go down only three layers, the other two branches go down four layers.
First, we prepare the various inputs:
% Controls
bl_verbose = true;
bl_bfw_model = true;
% Given rho and beta, solve for equilibrium quantities
mp_func = bfw_mp_func_demand();
% Following instructions in: PrjFLFPMexicoBFW\solvedemand\README.md
% Nests/layers
it_nests = 4;
% Input cell of mn matrixes
it_prho_cl = 1;
it_pshare_cl = 2;
it_yz_share_cl = 3;
for it_cl_ctr = [1,2,3]
cl_mn_cur = cell(it_nests,1);
% Fill each cell element with NaN mn array
for it_cl_mn = 1:it_nests
bl_yz_share = (it_cl_ctr == it_yz_share_cl);
if (~bl_yz_share && it_cl_mn == 1)
mn_nan = NaN;
elseif (~bl_yz_share && it_cl_mn == 2) || (bl_yz_share && it_cl_mn == 1)
mn_nan = [NaN, NaN];
elseif (~bl_yz_share && it_cl_mn == 3) || (bl_yz_share && it_cl_mn == 2)
mn_nan = NaN(2,2);
elseif (~bl_yz_share && it_cl_mn == 4) || (bl_yz_share && it_cl_mn == 3)
mn_nan = NaN(2,2,2);
elseif (~bl_yz_share && it_cl_mn == 5) || (bl_yz_share && it_cl_mn == 4)
mn_nan = NaN(2,2,2,2);
elseif (~bl_yz_share && it_cl_mn == 6) || (bl_yz_share && it_cl_mn == 5)
mn_nan = NaN(2,2,2,2,2);
end
cl_mn_cur{it_cl_mn} = mn_nan;
end
% Name cell arrays
if (it_cl_ctr == it_prho_cl)
cl_mn_prho = cl_mn_cur;
elseif (it_cl_ctr == it_pshare_cl)
cl_mn_pshare = cl_mn_cur;
elseif (it_cl_ctr == it_yz_share_cl)
cl_mn_yz_choices = cl_mn_cur;
end
end
% Initialize share matrix
rng(123);
for it_cl_mn = 1:it_nests
mn_pshare = cl_mn_pshare{it_cl_mn};
if it_cl_mn == 4
mn_pshare(2,:,:) = rand(2,2);
else
mn_pshare = rand(size(mn_pshare));
end
cl_mn_pshare{it_cl_mn} = mn_pshare;
end
% Initialize rho matrix
rng(456);
for it_cl_mn = 1:it_nests
mn_prho = cl_mn_prho{it_cl_mn};
if it_cl_mn == 4
mn_prho(2,:,:) = rand(2,2);
else
mn_prho = rand(size(mn_prho));
end
% Scalling rho between 0.7500 and -3.0000
% 1 - 2.^(linspace(-2,2,5))
mn_prho = 1 - 2.^(mn_prho*(4) - 2);
cl_mn_prho{it_cl_mn} = mn_prho;
end
% Initialize quantities matrix
rng(789);
for it_cl_mn = 1:it_nests
mn_yz_choices = cl_mn_yz_choices{it_cl_mn};
if it_cl_mn == 3
mn_yz_choices(1,:,:) = rand(2,2);
elseif it_cl_mn == 4
mn_yz_choices(2,:,:,:) = rand(2,2,2);
end
% Scalling quantities between 3 amd 5
mn_yz_choices = mn_yz_choices*(2) + 3;
cl_mn_yz_choices{it_cl_mn} = mn_yz_choices;
end
% Initialize yz matrix
rng(101112);Second, display created inputs:
celldisp(cl_mn_prho);
cl_mn_prho{1} =
0.5017
cl_mn_prho{2} =
0.6071 -1.1955
cl_mn_prho{3} =
-1.3523 -0.3346
-0.4167 -1.9136
cl_mn_prho{4} =
(:,:,1) =
NaN NaN
-1.0512 0.5869
(:,:,2) =
NaN NaN
0.6209 0.1633
celldisp(cl_mn_pshare);
cl_mn_pshare{1} =
0.6965
cl_mn_pshare{2} =
0.2861 0.2269
cl_mn_pshare{3} =
0.5513 0.4231
0.7195 0.9808
cl_mn_pshare{4} =
(:,:,1) =
NaN NaN
0.6848 0.4809
(:,:,2) =
NaN NaN
0.3921 0.3432
celldisp(cl_mn_yz_choices);
cl_mn_yz_choices{1} =
NaN NaN
cl_mn_yz_choices{2} =
NaN NaN
NaN NaN
cl_mn_yz_choices{3} =
(:,:,1) =
3.6467 3.4605
NaN NaN
(:,:,2) =
4.5876 4.2488
NaN NaN
cl_mn_yz_choices{4} =
(:,:,1,1) =
NaN NaN
4.9508 4.5178
(:,:,2,1) =
NaN NaN
3.0212 3.0495
(:,:,1,2) =
NaN NaN
3.2221 4.0763
(:,:,2,2) =
NaN NaN
3.0909 4.1031Third, call function and solve for optimal demand:
% Call function
[cl_mn_yz_choices, cl_mn_mpl_price] = ...
bfw_crs_nested_ces_mpl(cl_mn_prho, cl_mn_pshare, cl_mn_yz_choices, ...
mp_func, bl_verbose, bl_bfw_model);
----------------------------------------
xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
CONTAINER NAME: mp_container_map ND Array (Matrix etc)
xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
i idx ndim numel rowN colN sum mean std coefvari min max
__ ___ ____ _____ ____ ____ ________ ________ ________ ________ _________ ________
mpl_price_c1 1 1 2 2 1 2 1.0002 0.5001 0.28686 0.57362 0.29725 0.70294
mpl_price_c2 2 2 2 4 2 2 1.0009 0.25022 0.17949 0.71731 0.080381 0.50351
mpl_price_c3 3 3 3 8 2 4 1.0088 0.1261 0.10191 0.80822 0.0063057 0.25809
mpl_price_c4 4 4 4 16 2 8 NaN NaN NaN NaN 0.0025507 0.11203
prho_c2 5 6 2 2 1 2 -0.58844 -0.29422 1.2746 -4.3323 -1.1955 0.60709
prho_c3 6 7 2 4 2 2 -4.0173 -1.0043 0.76195 -0.75868 -1.9136 -0.33464
prho_c4 7 8 3 8 2 4 NaN NaN NaN NaN -1.0512 0.62089
pshare_c2 8 10 2 2 1 2 0.51299 0.2565 0.041923 0.16344 0.22685 0.28614
pshare_c3 9 11 2 4 2 2 2.6747 0.66866 0.24087 0.36023 0.42311 0.98076
pshare_c4 10 12 3 8 2 4 NaN NaN NaN NaN 0.34318 0.68483
yz_c1 11 13 2 2 1 2 8.0897 4.0448 0.173 0.04277 3.9225 4.1672
yz_c2 12 14 2 4 2 2 16.015 4.0039 0.19166 0.04787 3.8468 4.2727
yz_c3 13 15 3 8 2 4 31.235 3.9044 0.51337 0.13149 3.0635 4.5876
yz_c4 14 16 4 16 2 8 NaN NaN NaN NaN 3.0212 4.9508
xxx TABLE:mpl_price_c1 xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
c1 c2
_______ _______
r1 0.70294 0.29725
xxx TABLE:mpl_price_c2 xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
c1 c2
________ _______
r1 0.19946 0.50351
r2 0.080381 0.21754
xxx TABLE:mpl_price_c3 xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
c1 c2 c3 c4
________ _______ ________ _________
r1 0.13727 0.24893 0.065108 0.25809
r2 0.050551 0.21139 0.031132 0.0063057
xxx TABLE:mpl_price_c4 xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
c1 c2 c3 c4 c5 c6 c7 c8
_______ ________ ________ _________ ________ _______ ________ _________
r1 NaN NaN NaN NaN NaN NaN NaN NaN
r2 0.02507 0.099481 0.012272 0.0025507 0.027845 0.11203 0.018861 0.0038085
xxx TABLE:prho_c2 xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
c1 c2
_______ _______
r1 0.60709 -1.1955
xxx TABLE:prho_c3 xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
c1 c2
________ ________
r1 -1.3523 -0.33464
r2 -0.41668 -1.9136
xxx TABLE:prho_c4 xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
c1 c2 c3 c4
_______ _______ _______ _______
r1 NaN NaN NaN NaN
r2 -1.0512 0.58694 0.62089 0.16334
xxx TABLE:pshare_c2 xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
c1 c2
_______ _______
r1 0.28614 0.22685
xxx TABLE:pshare_c3 xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
c1 c2
_______ _______
r1 0.55131 0.42311
r2 0.71947 0.98076
xxx TABLE:pshare_c4 xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
c1 c2 c3 c4
_______ _______ _______ _______
r1 NaN NaN NaN NaN
r2 0.68483 0.48093 0.39212 0.34318
xxx TABLE:yz_c1 xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
c1 c2
______ ______
r1 3.9225 4.1672
xxx TABLE:yz_c2 xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
c1 c2
______ ______
r1 4.0073 3.8887
r2 3.8468 4.2727
xxx TABLE:yz_c3 xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
c1 c2 c3 c4
______ ______ ______ ______
r1 3.6467 3.4605 4.5876 4.2488
r2 4.23 4.2863 3.0635 3.7118
xxx TABLE:yz_c4 xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
c1 c2 c3 c4 c5 c6 c7 c8
______ ______ ______ ______ ______ ______ ______ ______
r1 NaN NaN NaN NaN NaN NaN NaN NaN
r2 4.9508 4.5178 3.0212 3.0495 3.2221 4.0763 3.0909 4.1031
----------------------------------------
xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
CONTAINER NAME: mp_container_map Scalars
xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
i idx value
_ ___ _______
prho_c1 1 5 0.50172
pshare_c1 2 9 0.69647